Introduction
Welcome to Pistonudos.com, where we are passionate about the world of cars and everything related to driving. In this article, we are going to explore the differences and classifications of secondary, primary and tertiary roads, as well as provide useful information on driving on secondary roads and understanding the types of secondary and tertiary roads and streets in different locations.
What are secondary, primary and tertiary pathways?
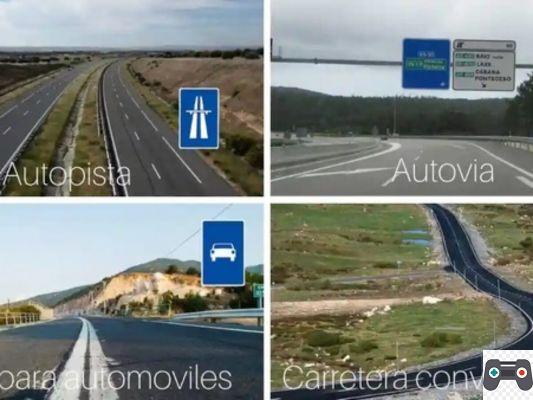
Before delving into the differences between these pathways, it is important to understand what is meant by each of them. Secondary roads are those that connect rural and urban areas, generally with less traffic capacity and lower speed allowed. On the other hand, primary roads are the main highways that connect cities and regions, with greater traffic capacity and allowed speed. Finally, tertiary roads are smaller and less traveled roads, which are usually used to access remote or difficult-to-reach areas.
Differences Between Secondary, Primary, and Tertiary Pathways
The differences between these roads lie mainly in their function, traffic capacity and allowed speed. Secondary roads tend to have lighter traffic and a lower maximum permitted speed, as they are designed to connect local areas and allow access to rural areas. On the other hand, primary roads have a higher traffic flow and a higher maximum permitted speed, since their main function is to connect cities and regions efficiently. Tertiary roads, for their part, are smaller and less traveled roads, with an even lower traffic capacity and a lower maximum permitted speed.
Tips for driving on back roads
Driving on back roads can be an enjoyable and scenic experience, but it also requires caution and attention. Here are some tips for driving safely on these roads:
- Maintain an appropriate speed: Secondary roads often have sharp curves and slope changes, so it is important to adapt your speed to the road conditions.
- Respect traffic signs: Make sure you follow the maximum speed indications, overtaking allowed and any other signs present on the road.
- Use the right lights: In case of driving at night or in low visibility conditions, make sure to turn on the vehicle's lights to be visible to other drivers.
- Keep a safe distance: As on any other road, it is important to maintain an adequate distance from the vehicle that precedes you in order to react to any unforeseen event.
Types of secondary and tertiary roads and streets in different places
Secondary and tertiary roads and streets can vary in design and characteristics depending on where you are. Here are some examples of these types of roads in different countries:
United States
In the United States, feeder roads are typically state or rural highways that connect local areas and allow access to rural areas. On the other hand, the primary highways are the famous interstates or interstate highways that connect cities and regions throughout the country. Tertiary roads can be dirt roads or small highways that lead to remote or hard-to-reach areas.
Spain
In Spain, secondary roads are known as regional roads and connect rural and urban areas within the same region. Primary roads are the dual carriageways and highways that connect cities and regions efficiently. Tertiary roads can be country roads or forest tracks that allow access to natural or rural areas.
Japan
In Japan, secondary roads are known as prefectural highways and connect local areas within a single prefecture. Primary highways are the national highways that connect cities and regions throughout the country. Tertiary roads can be mountain roads or country roads leading to remote or tourist areas.
Frequent questions
1. What is the difference between a secondary road and a tertiary road?
The main difference between a secondary road and a tertiary road lies in its traffic capacity and allowed speed. Secondary roads tend to have a higher traffic flow and a higher maximum permitted speed than tertiary roads. In addition, secondary roads often connect rural and urban areas, while tertiary roads are smaller, less-traveled roads that lead to remote or hard-to-reach areas.
2. What is the importance of knowing the differences between these pathways?
It is important to know the differences between secondary, primary and tertiary roads in order to plan driving routes efficiently and safely. In addition, understanding the characteristics of each type of road allows us to adapt our driving to the road conditions and respect the established traffic regulations. Knowing these differences also helps us make informed decisions when choosing the most appropriate route for our destination.
Conclusion
In summary, secondary, primary and tertiary roads have significant differences in terms of their function, traffic capacity and allowed speed. Driving on secondary roads requires caution and adaptation to road conditions, while primary roads are the main connecting arteries between cities and regions. Tertiary highways, meanwhile, are smaller, less-traveled roads that lead to remote areas. Knowing these differences allows us to plan our driving routes efficiently and safely.
We hope this article has been informative and helpful in understanding the differences and classifications of secondary, primary, and tertiary pathways. If you have any additional questions or want to share your experience, feel free to leave us a comment below. We would love to hear your opinion!
Until next time, car lovers!